Best Recipes for People with Gout
Mediterranean Quinoa Salad
This vibrant salad is a delightful and healthy option for gout sufferers. Quinoa, a complete protein, provides sustained energy without the inflammatory compounds often found in red meat. The fresh vegetables like cucumber, tomatoes, and bell peppers are packed with vitamins and antioxidants, promoting overall health and well-being. A light lemon vinaigrette adds a zesty flavor without the high purine content often present in rich dressings. This salad is easily customizable, allowing you to add your favorite vegetables and herbs for a unique twist.
The combination of protein from quinoa and the hydrating nature of the vegetables makes it a perfect meal for managing gout symptoms. It's a great option for lunch or a light dinner, offering a delicious and satisfying way to nourish your body without triggering gout flare-ups.
Creamy Roasted Vegetable Soup
This creamy, yet low-purine, vegetable soup is a comforting and flavorful way to enjoy a gout-friendly meal. Roasted vegetables like carrots, zucchini, and sweet potatoes bring a depth of flavor, while a touch of coconut milk adds a creamy texture without the inflammatory effects of dairy. The soup is packed with essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health and well-being.
The roasting process intensifies the natural sweetness of the vegetables, creating a harmonious and satisfying flavor profile. This soup is easily adaptable, allowing you to experiment with different vegetable combinations and spices to create your own unique variations. It's perfect for a comforting weeknight dinner, promoting a healthy and gout-friendly eating experience.
Asparagus and Chickpea Curry
This flavorful curry features asparagus and chickpeas, providing a delicious and nutritious meal option for gout sufferers. The asparagus is a low-purine vegetable, while chickpeas offer a good source of plant-based protein. The curry's mild spices contribute to a savory and aromatic flavor experience. A touch of ginger and garlic adds a depth of flavor without impacting gout symptoms.
Garlic-Roasted Asparagus with Lemon
This simple yet elegant dish showcases the delicate flavor of asparagus. Roasting the asparagus brings out its natural sweetness, while a squeeze of lemon juice adds a bright and zesty touch. This recipe is incredibly quick and easy to prepare, making it a perfect weeknight meal option for gout sufferers. The low purine content of asparagus makes it a safe and healthy addition to your gout-friendly diet.
Zucchini Noodles with Tomato Sauce
A light and refreshing dish perfect for a quick and healthy meal. Zucchini noodles provide a low-carb alternative to pasta, while a flavorful tomato sauce adds a satisfying touch. You can easily customize the sauce with herbs and spices to create your own unique flavor combinations. This dish is packed with vitamins and minerals, promoting overall health and well-being while being gentle on your gout.
Experimental research designs are characterized by the researcher manipulating one or more independent variables to observe their effect on a dependent variable. This manipulation typically occurs under controlled conditions, allowing researchers to isolate the impact of the independent variable and minimize the influence of extraneous factors. A crucial aspect of experimental designs is the random assignment of participants to different conditions, ensuring that the groups are as similar as possible at the outset. This randomization helps to establish causality, as any observed differences in the dependent variable can be attributed to the manipulation of the independent variable. Different experimental designs, such as pre-test/post-test designs, control group designs, and factorial designs, offer varying levels of control and complexity, each suited to specific research questions.
Smart Carb Choices for Gout Management
Understanding Smart Carb Choices
When managing gout, focusing on smart carb choices is crucial. It's not about eliminating carbohydrates entirely, but rather selecting those that have a lower impact on your body's uric acid levels. This means prioritizing complex carbohydrates over simple sugars. Complex carbohydrates are broken down more slowly, releasing glucose gradually into the bloodstream, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels and potentially reduce the risk of gout flare-ups.
Simple sugars, found in processed foods and sugary drinks, are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a sharp spike in blood sugar and potentially triggering uric acid production. Making informed choices about the types of carbohydrates you consume can significantly benefit your gout management plan.
Low-Impact Carbohydrate Sources
Excellent choices for managing gout include whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats. These provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber, which aids in digestion and can help regulate blood sugar. Legumes, such as beans and lentils, are also a good source of complex carbohydrates and protein. They are packed with nutrients and contribute to a balanced diet for overall health.
Fruits like berries, apples, and pears can be included in moderation. While they contain natural sugars, they also offer valuable vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Portion control is key, ensuring you're not consuming excessive amounts of fruit, which could potentially impact your gout management.
Avoiding High-Impact Carbs
Foods like white bread, white rice, and pastries are generally best avoided due to their high glycemic index. These simple carbohydrates are rapidly digested, leading to a rapid increase in blood sugar and potentially triggering a gout attack. Sugary drinks, including sodas and fruit juices, should also be limited. These drinks are often high in fructose, a type of sugar that can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
The Role of Portion Control
Even with smart carb choices, portion control remains essential in gout management. While certain carbohydrates are better choices than others, consuming large portions of any carbohydrate can still negatively impact your uric acid levels. Paying attention to serving sizes and mindful eating can significantly contribute to effectively managing gout and minimizing flare-ups. A balanced approach that considers both the type and quantity of carbohydrates is crucial for a successful gout management strategy.
Ultimately, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance on creating a gout-friendly meal plan that aligns with your specific needs and dietary preferences. They can help you tailor your carbohydrate intake to effectively manage your gout.
Flavorful Recipes for Gout-Friendly Living: Practical Examples

Reducing Purine Intake for Gout Management
A cornerstone of gout management is minimizing purine consumption. Purines are naturally occurring compounds found in certain foods that, when broken down, produce uric acid. High levels of uric acid are the primary culprit behind gout attacks. Understanding which foods are high in purines and making conscious choices to limit their intake is crucial for managing gout symptoms and preventing future flare-ups.
Identifying and avoiding high-purine foods such as organ meats, shellfish, and some types of fish is key. Furthermore, consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain overall health and support the body's natural processes.
The Importance of Hydration in Gout Prevention
Adequate hydration is absolutely essential for flushing out excess uric acid from the body. Drinking plenty of water helps to dilute uric acid levels, preventing it from crystallizing and forming painful deposits in the joints. Maintaining a consistent intake of water throughout the day is paramount for gout management.
Delicious Low-Purine Vegetable Dishes
Fortunately, many delicious and nutritious foods are naturally low in purines. Vegetables are an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, offering substantial health benefits without contributing to the uric acid buildup that triggers gout attacks. Think vibrant salads, hearty stews, and flavorful stir-fries. These dishes are not only gout-friendly but also contribute to a balanced and healthy diet.
Lean Protein Choices for Gout Patients
While high-purine protein sources must be limited, lean protein sources like poultry (without skin) and fish (excluding shellfish) are still acceptable options. These options provide the necessary protein for muscle repair and growth without significantly increasing uric acid production.
Careful portion control is important when incorporating these protein options into your diet plan for gout management. The goal is to find a balance that supports overall health without exacerbating gout symptoms.
Strategic Carbohydrate Intake
Choosing the right carbohydrates can significantly impact gout management. Focus on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for a balanced carbohydrate intake. These options provide essential nutrients without contributing to a rapid rise in blood sugar levels, which can indirectly affect gout.
The Role of Healthy Fats in Gout Management
Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, play a vital role in overall health. Incorporating these fats into a gout-friendly diet can promote satiety and contribute to a balanced nutritional intake. However, it's crucial to consume them in moderation, as some fats can indirectly affect uric acid levels. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate intake for your specific needs.
Read more about Best Recipes for People with Gout
Hot Recommendations
- Traditional Foods for Day of the Dead
- Food Etiquette in Italy: Pasta Rules!
- Best Family Friendly Restaurants with Play Areas in [City]
- Review: The Best [Specific Dessert] Place in [City]
- Top Ice Cream Parlors in [City]
- Traditional Foods for Halloween
- The History of the Potato in Ireland
- Best Vegan Pizza Joints in [City] [2025]
- Best Bakeries for Sourdough Bread in [City]
- Food Culture in Argentina: Asado and Wine




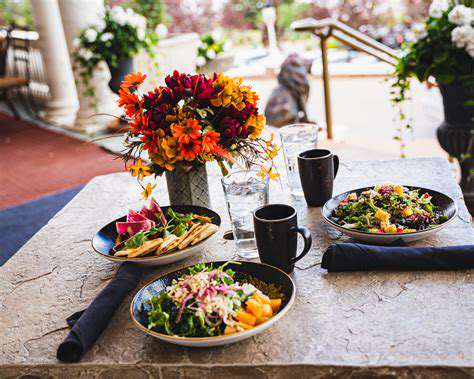





![[Brand A] Air Fryer vs [Brand B] Air Fryer: Which is Better?](/static/images/28/2025-07/ValueforMoneyandWarranty.jpg)