Healthy Eating for People with Acid Reflux
Understanding the Connection Between Diet and Acid Reflux
Acid reflux, a common digestive issue, often stems from the interaction between certain foods and your body's natural processes. Identifying these trigger foods is crucial for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. Understanding the physiological mechanisms behind acid reflux—how certain foods irritate the esophageal lining and trigger acid to flow back into the esophagus—is the first step toward effective dietary management.
Different individuals react differently to various foods. What might be a benign food for one person can be a significant trigger for another. This highlights the personalized nature of dietary management for acid reflux.
Common Culprits: Identifying Trigger Foods
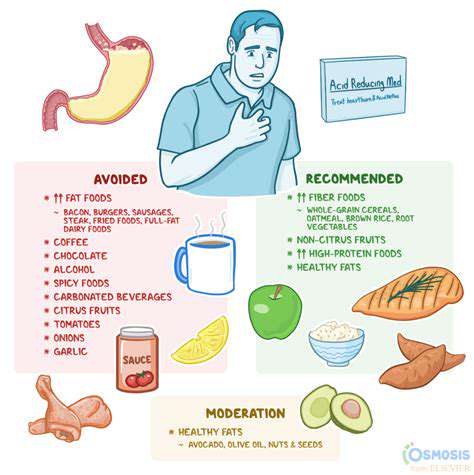
Many foods are known to exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. These include highly acidic foods like citrus fruits, tomatoes, and vinegar-based dressings. Spicy foods, particularly those containing chili peppers and other strong spices, often trigger a burning sensation in the esophagus due to their effect on stomach acid production.
Fatty and fried foods can also contribute to acid reflux. These foods often take longer to digest, which can increase stomach pressure and lead to acid reflux episodes.
Beyond the Obvious: Less Recognized Trigger Foods
While citrus fruits and spicy dishes are frequently identified as culprits, some less obvious foods can also trigger acid reflux. Chocolate, for example, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is the muscle that prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. Alcohol, particularly in excess, can also negatively impact the LES, making it more prone to malfunction and increasing the risk of acid reflux.
The Role of Caffeine and Carbonation
Caffeine, a stimulant found in coffee, tea, and some sodas, can stimulate stomach acid production. This increased acid production can contribute to acid reflux symptoms in susceptible individuals. Carbonated beverages, with their bubbles and the release of carbon dioxide in the stomach, can also put pressure on the LES, potentially causing acid reflux.
Dietary Strategies for Symptom Management
Adopting a diet specifically designed to minimize acid reflux triggers is essential for long-term symptom management. This involves gradually eliminating potential trigger foods from your diet and paying close attention to how your body reacts.
Keeping a food diary can help identify patterns and pinpoint specific foods that exacerbate your symptoms. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and a tailored dietary plan for effective symptom management.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Holistic Relief
Managing acid reflux often involves more than just dietary changes. Lifestyle factors play a significant role. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding large meals, and eating meals more slowly can all help reduce the pressure on the LES. Elevating the head of your bed by a few inches can also help prevent acid reflux during sleep.
Stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, can also be beneficial for reducing the likelihood of acid reflux episodes. Regular exercise and a balanced lifestyle are crucial for overall digestive health and minimizing acid reflux triggers.
The Impact of Beverages on Acid Reflux Symptoms
The Role of Acidic Beverages in Stomach Acid Production
Beverages play a significant role in influencing the levels of stomach acid, which is crucial for digestion. Highly acidic drinks can trigger an increase in gastric acid secretion, potentially leading to discomfort and even complications for individuals with pre-existing conditions such as acid reflux or gastritis. Understanding the impact of different beverages on stomach acid production is important for maintaining digestive health. Several factors, including the acidity level of the beverage, the individual's sensitivity, and the overall dietary intake, contribute to this complex interplay.
The consumption of acidic beverages, such as fruit juices, sodas, and even some types of coffee, can stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This increased acidity can exacerbate symptoms for those prone to acid reflux or heartburn. It's important to note that while some acidity is necessary for proper digestion, excessive acidity can lead to various digestive issues. The impact of specific beverages varies from person to person, highlighting the importance of individual dietary considerations and potential sensitivities.
The Influence of Beverage Choices on Digestive Health
Choosing beverages wisely can significantly impact digestive health. Opting for beverages with lower acidity, such as water, milk, or herbal teas, can promote a healthier digestive environment. These options are generally gentler on the stomach lining and less likely to provoke an overproduction of stomach acid. Moreover, the consumption of water is essential for hydration and overall bodily function, playing a crucial role in supporting healthy digestion.
The sugar content of beverages also plays a role. Sugary drinks, including sodas and some fruit juices, can contribute to digestive issues, such as bloating and gas. They can also negatively affect blood sugar levels, which can indirectly impact digestive health. Mindful beverage choices can significantly influence the well-being of the digestive system. Therefore, selecting beverages with minimal acidity and sugar content is often a key strategy for maintaining optimal digestive health.
The temperature of beverages can also affect digestion. Extremely hot or cold beverages can sometimes irritate the sensitive lining of the esophagus and stomach, potentially contributing to discomfort or even more serious issues. A moderate temperature can be helpful for digestion.
Ultimately, understanding the individual impact of different beverages on digestion is key to promoting overall health. This knowledge can guide personalized dietary choices and help prevent or manage digestive issues.

Read more about Healthy Eating for People with Acid Reflux
Hot Recommendations
- Traditional Foods for Day of the Dead
- Food Etiquette in Italy: Pasta Rules!
- Best Family Friendly Restaurants with Play Areas in [City]
- Review: The Best [Specific Dessert] Place in [City]
- Top Ice Cream Parlors in [City]
- Traditional Foods for Halloween
- The History of the Potato in Ireland
- Best Vegan Pizza Joints in [City] [2025]
- Best Bakeries for Sourdough Bread in [City]
- Food Culture in Argentina: Asado and Wine



![Healthy Eating for Toddlers [Tips & Recipes]](/static/images/28/2025-05/FruitandVeggieFun.jpg)



![Top Spots for Oysters in [Coastal City]](/static/images/28/2025-05/CasualOysterBarsforaRelaxedAtmosphere.jpg)


