Health Benefits of Magnesium Rich Foods

Magnesium's Role in Bone Health and Blood Sugar Control
Magnesium's Crucial Role in Bone Formation
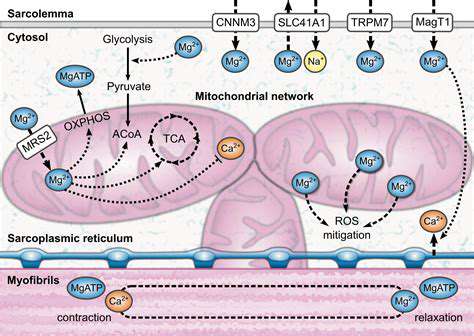
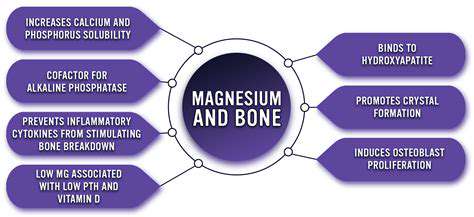
Magnesium plays a vital role in the complex process of bone formation and maintenance. It's essential for the proper functioning of enzymes involved in collagen synthesis, a crucial protein that provides structure and flexibility to bones. Without adequate magnesium, the body struggles to build strong, healthy bones, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis. This vital mineral directly influences calcium absorption and utilization, which are both critical for bone density.
Bone cells, osteoblasts, rely on magnesium for their activity. These cells are responsible for building new bone tissue, ensuring ongoing repair and growth. Adequate magnesium levels are therefore paramount for maintaining the integrity of the skeletal system throughout life.
Magnesium's Influence on Bone Remodeling
Bone remodeling is a continuous process of bone resorption (breakdown) and formation (creation), ensuring the bone structure remains strong and adaptable. Magnesium is instrumental in this dynamic process. It regulates the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption, ensuring a balanced turnover of bone tissue.
This finely tuned balance is critical for maintaining bone health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Magnesium also supports the proper function of osteoblasts, the cells that build new bone, ensuring a healthy equilibrium in this crucial process.
Magnesium and Calcium Interaction in Bone Health
Magnesium and calcium are closely intertwined in their role in bone health. Calcium, while often highlighted, cannot function optimally without adequate magnesium. Magnesium is required for calcium absorption and transport into the bone tissue. This synergistic relationship highlights the importance of maintaining balanced levels of both minerals for optimal bone health.
Inadequate magnesium can hinder calcium's incorporation into bone, leading to weakened bone structure and increased risk of fractures. Conversely, sufficient magnesium ensures calcium is effectively utilized, resulting in denser, healthier bones.
Magnesium's Impact on Bone Mineral Density
Bone mineral density (BMD) is a key indicator of bone health. Higher BMD generally correlates with a lower risk of fractures. Magnesium plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal BMD. It supports the incorporation of calcium and phosphate into the bone matrix, strengthening the overall structure and density.
Sufficient magnesium intake contributes to a higher BMD, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and related fractures, especially as we age. This is particularly important for individuals at risk for osteoporosis, as magnesium can help mitigate the loss of bone density associated with aging.
Magnesium Deficiency and its Impact on Bone Health
Magnesium deficiency, a relatively common nutritional concern, can have a significant negative impact on bone health. Insufficient magnesium levels disrupt the delicate balance of bone remodeling, leading to a decreased rate of bone formation and an increased rate of bone resorption.
This imbalance results in weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures and contributing to conditions like osteoporosis. Identifying and addressing magnesium deficiency is therefore crucial for maintaining overall skeletal health and preventing future complications.
A diet rich in magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds is essential for maintaining optimal magnesium levels and supporting healthy bone development and maintenance. Regular intake of magnesium-rich foods and appropriate dietary supplements can assist in preventing and addressing magnesium deficiency, promoting robust bone health.
Read more about Health Benefits of Magnesium Rich Foods
Hot Recommendations
- Traditional Foods for Day of the Dead
- Food Etiquette in Italy: Pasta Rules!
- Best Family Friendly Restaurants with Play Areas in [City]
- Review: The Best [Specific Dessert] Place in [City]
- Top Ice Cream Parlors in [City]
- Traditional Foods for Halloween
- The History of the Potato in Ireland
- Best Vegan Pizza Joints in [City] [2025]
- Best Bakeries for Sourdough Bread in [City]
- Food Culture in Argentina: Asado and Wine









![Seasonal Ingredient Guide for Winter [2025]](/static/images/28/2025-06/CitrusFruits3AABurstofWinterSunshine.jpg)
